Background Restriction Android
- Background Data Restriction Android
- Life360 Background Restriction Android
- Background Restriction Android Pie
- It is a tough call – and personal choice – to decide whether or not you wish to restrict the data usage of certain apps. Research each one to see what is and is not transmitted when they are not in use, and decide which ones you can safely disable. Use these steps to disable background data on the Samsung Galaxy S10. WiFi Background Data.
- For disabling background data for all the apps at a time, head over to Settings menu where you can find the option Data usage. Tap on it and you can find a graph which clearly depicts the data consumption in your android. You can monitor your data usage from here by settings cycles, can also set warnings and can enable or disable mobile data.
- 'Background Restriction' (or 'Allow Background Activity' on some devices) is intended to stop ALL background activity regardless of whether your service has called setForeground There is no way around this setting. You cannot programmatically disable it.
'Background Restriction' (or 'Allow Background Activity' on some devices) is intended to stop ALL background activity regardless of whether your service has called setForeground There is no way around this setting. You cannot programmatically disable it.
In Android 9 and higher, the platform can monitor apps for behavior thatnegatively affects the battery life of devices. The platform uses andevaluates setup rules to provide a UX flow that gives users the option torestrict apps that violate the rules.
In Android 8.0 and lower, there were restrictions through featuressuch as Doze, app standby, background limits, and background locationlimits. However, some apps continued to exhibit bad behaviors, some ofwhich are described in Android vitals.Android 9 introduced an OS infrastructure that can detect and restrictapps based on setup rules that can be updated over time.

Background restrictions

Users can restrict apps, or the system may suggest apps that it detects are negatively impacting the health of the device.
Restricted apps:
- Can still be launched by the user.
- Can't run jobs/alarms or use the network in the background.
- Can't run foreground services.
- Can be changed to an unrestricted app by the user.
Device implementers can add additional restrictions to apps to:
- Restrict the app from self restarts.
- Restrict services from being bound (highly risky).
Restricted apps in the background aren't expected to consume any device resources, such as memory, CPU, and battery. Background-restricted apps shouldn't impact the device health when the user isn't actively using those apps. However, the same apps are expected to be fully functional when the user launches the apps.
Using custom implementations

Device implementers can continue to use their custom methods to apply restrictions on the apps.
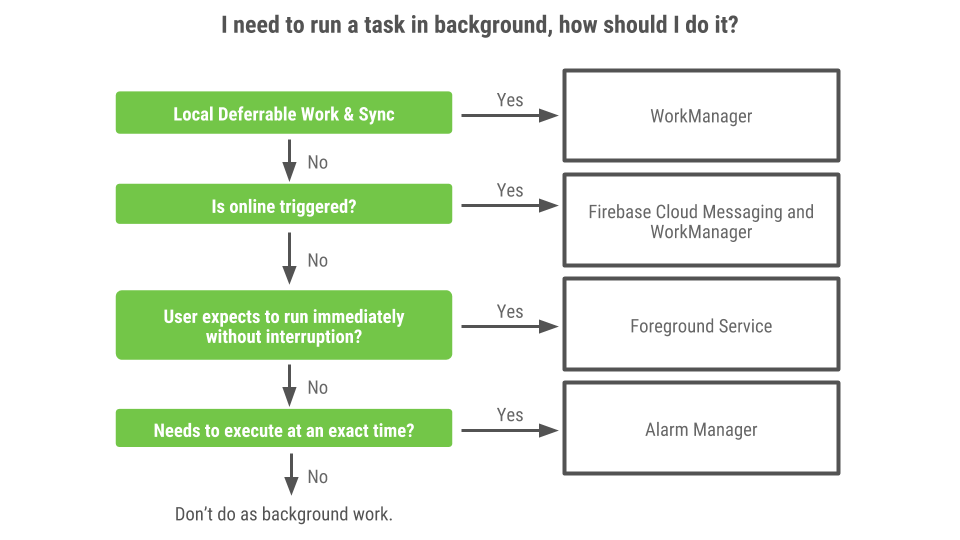
Caution: Future releases may break device implementers' customizations. We recommend adopting the Android 9 app restrictions architecture in AOSP.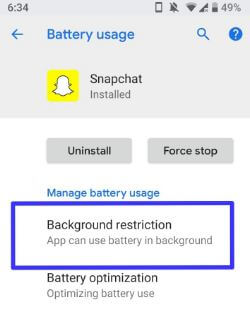
Integrating app restrictions
The following sections outline how to define and integrate app restrictions on your device. If you're using app restriction methods from Android 8.x or lower, review the following sections closely for changes in Android 9 and higher.
Background Data Restriction Android
Setting the AppOpsManager flag
When an app is restricted, set the appropriate flag in AppOpsManager. An example code snippet from packages/apps/Settings/src/com/android/settings/fuelgauge/BatteryUtils.java:
Ensuring isBackgroundRestricted returns true
When an app is restricted, ensure that ActivityManager.isBackgroundRestricted() returns true.
Logging the reason for restriction
When an app is restricted, log the reasons for the restriction. Anexample code snippet of logging frompackages/apps/Settings/src/com/android/settings/fuelgauge/batterytip/actions/RestrictAppAction.java:
Replace type with the value from AnomalyType.
Device implementers can use the constants defined insrc/com/android/settings/fuelgauge/batterytip/StatsManagerConfig.java:
When the user or the system removes an app's restrictions, you mustlog the reasons for removing the restrictions. An example code snippet of logging frompackages/apps/Settings/src/com/android/settings/fuelgauge/batterytip/actions/UnrestrictAppAction.java:
Testing app restrictions
To test the behavior of app restrictions in Android 9 and higher, use one of thefollowing commands:
- Put an app into restriction:
- Take an app out of restriction and restore the default behavior:
- Make an app in the background go idle immediately:
- Add a package to
tempwhitelistfor a short duration: - Add/remove a package from the user whitelist:
- Check internal state of
jobschedulerand alarm manager:
App standby
App standby extends battery life by deferring background networkactivity and jobs for apps the user isn't actively using.
App standby lifecycle
Download srs audio sandbox crack. The platform detects inactive apps and places them in appstandby until the user begins actively engaging with the app.
During the detection phase, the platform detects that an app is inactive whenthe device isn't charging and the user hasn't launched the app directly orindirectly for a specific amount of clock time as well as a specific amount of screen-on time.(Indirect launches occur when a foreground app accesses a service in a second app.)
During app standby, the platform prevents apps from accessing the network morethan once a day, deferring app syncs and other jobs.
The platform exits the app from standby when:
Life360 Background Restriction Android
- The app becomes active.
- The device is plugged in and charging.
Active apps are unaffected by app standby. An app is active when it has:
- A process currently in the foreground (either as an activity or foreground service, or in use by another activity or foreground service), such as notification listener, accessibility services, live wallpaper, etc.
- A notification viewed by the user, such as in the lock screen or notification tray
- Been explicitly launched by the user
An app is inactive if none of the above activities has occurred for a periodof time.
Testing app standby
Background Restriction Android Pie
You can manually test app standby using the following adbcommands:
